Unleashing the Potential of E-Waste: Innovative Technologies for Printed Circuit Board Recycling

In the rapidly evolving world of technology, the ever-increasing consumption of electronic devices has resulted in a surge in electronic waste (e-waste). These discarded electronics pose significant environmental challenges due to the presence of hazardous materials and valuable minerals.
Among the most critical components of e-waste are printed circuit boards (PCBs). PCBs are essential for connecting electronic components and enabling the functioning of devices such as computers, smartphones, and televisions. However, they also contain a complex mix of materials, including metals, plastics, and toxic substances that require specialized recycling techniques.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 57767 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 601 pages |
Challenges and Opportunities in PCB Recycling
PCB recycling presents unique challenges due to the intricate nature of these components. The traditional methods of recycling, such as incineration or landfilling, often result in the loss of valuable materials and the release of harmful pollutants into the environment.
However, the recognition of PCBs as a potential resource has spurred the development of innovative recycling technologies. These technologies aim to recover both the valuable minerals and the reusable materials in PCBs, contributing to a more sustainable and circular economy.
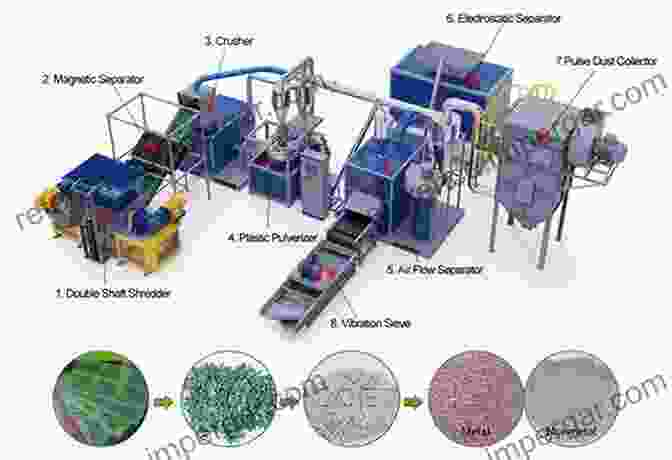
Innovative Recycling Technologies
- Hydrometallurgical Processes: These processes use chemical solvents to dissolve the metals in PCBs, separating them from the non-metallic materials. The metals can then be further refined to produce valuable commodities such as copper, gold, and silver.
- Pyrometallurgical Processes: These processes involve the controlled heating of PCBs in the presence of oxygen. The organic materials are burned away, leaving behind the metal oxides. The metal oxides can then be processed to recover the desired metals.
- Mechanical Separation Techniques: These techniques physically separate the different materials in PCBs using methods such as shredding, screening, and air classification. The recovered materials can be further purified and recycled into new products.
- Bioleaching Processes: These processes use microorganisms to dissolve the metals in PCBs. The microorganisms selectively extract the metals, leaving behind the non-metallic materials. Bioleaching is an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chemical leaching processes.
Benefits of PCB Recycling
The adoption of innovative PCB recycling technologies offers numerous benefits, including:
- Resource Conservation: Recycling PCBs helps conserve valuable natural resources by recovering metals and other materials that would otherwise be lost to disposal.
- Pollution Reduction: Recycling PCBs prevents the release of toxic substances into the environment, reducing the risk of soil and water contamination.
- Job Creation: The development and operation of PCB recycling facilities creates new employment opportunities in the waste management and recycling sector.
- Economic Growth: Recycling PCBs contributes to the circular economy by creating a new market for recycled materials and reducing the demand for raw materials.

The innovative technologies for printed circuit board recycling hold immense potential for addressing the challenges posed by electronic waste. These technologies enable the recovery of valuable minerals and materials, reducing the environmental impact and fostering a more sustainable future.
By promoting the adoption and development of these technologies, we can unlock the full potential of e-waste recycling and contribute to a cleaner, greener, and more circular economy.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 57767 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 601 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Daniel G Amen
Daniel G Amen Steve Nash
Steve Nash Shiva Swati
Shiva Swati James S Trefil
James S Trefil Tom Koob
Tom Koob Peter Duckers
Peter Duckers Richard Mant
Richard Mant Judy Capko
Judy Capko Pietro Moretti
Pietro Moretti Sean Mcmeekin
Sean Mcmeekin Michael D Floyd
Michael D Floyd Bruce A Markell
Bruce A Markell David Rose
David Rose Suzann Balduzzi
Suzann Balduzzi Alphadesigner
Alphadesigner Pierluigi Chiassoni
Pierluigi Chiassoni Rick Halpern
Rick Halpern Jordan Kassalow
Jordan Kassalow Sara J Van Ness
Sara J Van Ness Gloria Robertson
Gloria Robertson
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Russell MitchellCo Phase Traction Power Supply With Railway Hybrid Power Quality Conditioner
Russell MitchellCo Phase Traction Power Supply With Railway Hybrid Power Quality Conditioner
 Arthur C. ClarkeAn Autobiography of an Igbo Chief: A Journey Through History, Tradition, and...
Arthur C. ClarkeAn Autobiography of an Igbo Chief: A Journey Through History, Tradition, and...
 Nathaniel PowellNext Generation Self Emitting Displays: Revolutionizing the World of Visual...
Nathaniel PowellNext Generation Self Emitting Displays: Revolutionizing the World of Visual... Ralph Waldo EmersonFollow ·17.8k
Ralph Waldo EmersonFollow ·17.8k Bryce FosterFollow ·7.4k
Bryce FosterFollow ·7.4k Felix HayesFollow ·17.5k
Felix HayesFollow ·17.5k Ervin BellFollow ·17.6k
Ervin BellFollow ·17.6k Holden BellFollow ·15.6k
Holden BellFollow ·15.6k Jeffrey CoxFollow ·19.1k
Jeffrey CoxFollow ·19.1k Clark BellFollow ·11.2k
Clark BellFollow ·11.2k Dylan MitchellFollow ·14.9k
Dylan MitchellFollow ·14.9k

 Cade Simmons
Cade SimmonsUnlock Your Financial Future: Discover the Transformative...
In a tumultuous and ever-evolving financial...

 Cortez Reed
Cortez ReedBeyond Segregation: Multiracial and Multiethnic...
The United States has a long history of...

 Seth Hayes
Seth HayesUnlock the Secrets of Reflexology: A Journey to Stress...
Explore the...

 Tennessee Williams
Tennessee WilliamsLiminal Reality and Transformational Power: Exploring the...
Life is a constant...

 Jack London
Jack LondonUnlock the Secrets of Human Behavior: A Comprehensive...
Have you ever wondered...

 Rod Ward
Rod WardThe Philosopher's Gift: Reexamining Reciprocity
The concept of reciprocity, the idea that...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 57767 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 601 pages |