Thermosyphons and Heat Pipes: Theory and Applications: The Indispensable Guide for Thermal Engineers

In the realm of thermal engineering, the advent of thermosyphons and heat pipes has revolutionized the field of heat transfer. These passive devices harness the principles of evaporation and condensation to transport heat over considerable distances with unparalleled efficiency. This article delves into the intricate workings, applications, design considerations, and modeling techniques of thermosyphons and heat pipes, providing a comprehensive resource for engineers, researchers, and industry professionals.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 66163 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 626 pages |
Understanding Thermosyphons
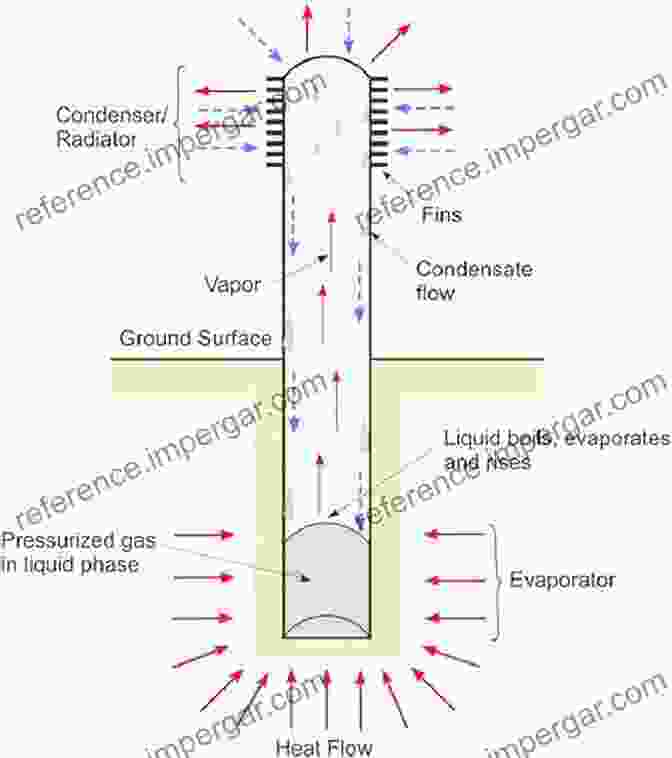
A thermosyphon is a passive heat transfer device that operates on the fundamental principles of natural convection. It consists of a sealed container containing a working fluid and a heat source at its base. As the heat source elevates the temperature of the working fluid, it vaporizes, creating a low-density vapor region at the top of the container. The vapor rises due to buoyancy forces, while the cooler, denser liquid falls back to the bottom, creating a continuous circulation loop. This natural convection mechanism enables thermosyphons to effectively transfer heat from the heat source to a heat sink located at the upper end of the container.
Advantages of Thermosyphons
- Passive Operation: Thermosyphons do not require any external power sources or moving parts, making them reliable and low-maintenance.
- High Thermal Efficiency: The continuous circulation of the working fluid eliminates thermal resistance, resulting in exceptional heat transfer rates.
- Compact Size and Low Cost: Thermosyphons are typically small and affordable, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Long-Distance Heat Transfer: Thermosyphons can effectively transport heat over distances of several meters, unlike conventional conduction methods.
- Low-Gravity Compatibility: Thermosyphons perform well in low-gravity environments, making them ideal for space applications.
Heat Pipe Technology
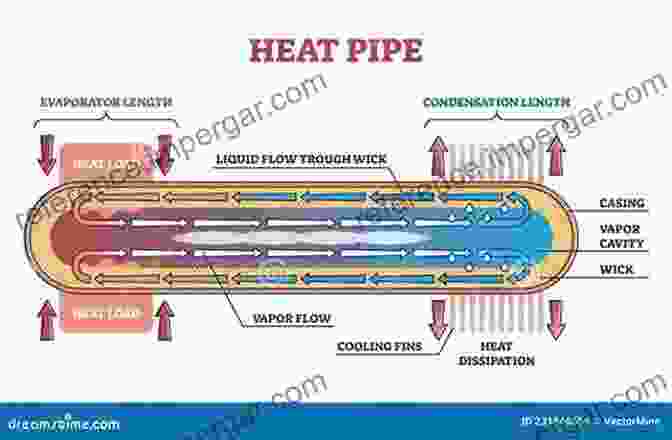
Heat pipes are advanced versions of thermosyphons that incorporate capillary structures to enhance their heat transfer capabilities. These structures, typically made of sintered metal or mesh wicks, provide a path for the working fluid to return from the condenser to the evaporator by capillary action. This eliminates the limitations of gravity-driven circulation, allowing heat pipes to operate effectively in any orientation.
Benefits of Heat Pipes
- Enhanced Heat Transfer: Capillary structures enable higher working fluid circulation, resulting in increased heat transfer rates.
- Compact Design: Heat pipes can achieve extremely high heat transfer rates in compact packages.
- Versatile Orientation: Heat pipes can operate in any orientation, providing greater design flexibility.
- Isothermal Operation: Heat pipes maintain a near-isothermal temperature along their length, enhancing thermal control.
- High Radiative Heat Transfer: Heat pipes can be designed with special coatings to enhance radiative heat transfer.
Applications of Thermosyphons and Heat Pipes
The versatility of thermosyphons and heat pipes has led to their widespread adoption in various industries, including:
- Electronics Cooling: Cooling high-power electronic components in laptops, smartphones, and servers.
- Thermal Management in Space: Regulating temperatures in satellites and spacecraft.
- Solar Thermal Systems: Harnessing solar energy for residential and industrial heating.
- Industrial Process Cooling: Efficiently cooling equipment in manufacturing processes.
- Geothermal Applications: Extracting heat from geothermal reservoirs for power generation.
Design Considerations for Thermosyphons and Heat Pipes
Optimizing the performance of thermosyphons and heat pipes requires careful consideration of several design parameters, including:
- Working Fluid Selection: Choosing an appropriate working fluid based on its physical properties, such as vapor pressure and thermal conductivity.
- Container Material and Geometry: Selecting materials that can withstand the operating temperature and ensure proper fluid flow.
- Wick Structure Design: Optimizing the wick structure to maximize capillary pumping and reduce pressure drop.
- Heat Source and Heat Sink Design: Ensuring efficient heat transfer at the evaporator and condenser sections.
- Non-Condensable Gas Management: Minimizing the presence of non-condensable gases to prevent performance degradation.
Modeling Techniques for Thermosyphons and Heat Pipes
Advanced modeling techniques are essential for accurately predicting the performance of thermosyphons and heat pipes. These techniques include:
- Analytical Modeling: Simplifying the system to derive analytical expressions for heat transfer rates and temperature profiles.
- Empirical Modeling: Using experimental data to develop empirical correlations for predicting performance.
- Numerical Modeling: Employing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to simulate complex fluid flow and heat transfer phenomena.
- Hybrid Modeling: Combining analytical, empirical, and numerical techniques to enhance accuracy.
Thermosyphons and heat pipes represent cutting-edge thermal engineering technologies with immense potential for revolutionizing heat transfer applications. Their passive operation, high efficiency, and versatility make them indispensable tools for engineers and researchers in diverse fields. This comprehensive guide has provided a detailed overview of the theory, applications, design considerations, and modeling techniques associated with thermosyphons and heat pipes. By mastering these concepts, engineers can unlock the full potential of these devices and drive innovation in various industries.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 66163 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 626 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia 10th Edition Kindle Edition
10th Edition Kindle Edition Julian Young
Julian Young Dzongsar Jamyang Khyentse
Dzongsar Jamyang Khyentse Geoffrey Bennett
Geoffrey Bennett Danielle Hawkins
Danielle Hawkins Sara J Van Ness
Sara J Van Ness Ali Omar Ali Mesrati
Ali Omar Ali Mesrati Jim Garrity
Jim Garrity Aseem Inam
Aseem Inam Ian Fletcher
Ian Fletcher Elizabeth Millard
Elizabeth Millard Orly Katz
Orly Katz Maudemarie Clark
Maudemarie Clark Jeremy Gilfor
Jeremy Gilfor Paul Slack
Paul Slack Prof Lyndon Neal Smith Phd
Prof Lyndon Neal Smith Phd Jim Carver
Jim Carver Josephine Humphreys
Josephine Humphreys Anna Hess
Anna Hess Patricia Overbaugh
Patricia Overbaugh
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 George R.R. MartinPhotobook to Enjoy the Leaves: A Visual Masterpiece of Autumn's Splendor
George R.R. MartinPhotobook to Enjoy the Leaves: A Visual Masterpiece of Autumn's Splendor
 Jack LondonUnraveling the Enigmatic World of Iran's Counterterrorism Elite: True Stories...
Jack LondonUnraveling the Enigmatic World of Iran's Counterterrorism Elite: True Stories... Griffin MitchellFollow ·5.9k
Griffin MitchellFollow ·5.9k Dwight BlairFollow ·2.6k
Dwight BlairFollow ·2.6k Gabriel BlairFollow ·15.7k
Gabriel BlairFollow ·15.7k Eugene PowellFollow ·3.9k
Eugene PowellFollow ·3.9k Langston HughesFollow ·11.3k
Langston HughesFollow ·11.3k Max TurnerFollow ·16.4k
Max TurnerFollow ·16.4k Edison MitchellFollow ·10.9k
Edison MitchellFollow ·10.9k Galen PowellFollow ·14.3k
Galen PowellFollow ·14.3k

 Cade Simmons
Cade SimmonsUnlock Your Financial Future: Discover the Transformative...
In a tumultuous and ever-evolving financial...

 Cortez Reed
Cortez ReedBeyond Segregation: Multiracial and Multiethnic...
The United States has a long history of...

 Seth Hayes
Seth HayesUnlock the Secrets of Reflexology: A Journey to Stress...
Explore the...

 Tennessee Williams
Tennessee WilliamsLiminal Reality and Transformational Power: Exploring the...
Life is a constant...

 Jack London
Jack LondonUnlock the Secrets of Human Behavior: A Comprehensive...
Have you ever wondered...

 Rod Ward
Rod WardThe Philosopher's Gift: Reexamining Reciprocity
The concept of reciprocity, the idea that...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 66163 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 626 pages |